Still have questions? Leave a comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Need
Editing and
Proofreading Services?

What Is Proofreading? Importance, Tips, Costs, and Examples
 Apr 23, 2024
Apr 23, 2024 7
min read
7
min read
Have you ever wondered why some texts seem clearer and more professional than others? The secret lies in proofreading. Proofreading elevates your content by eliminating errors and flaws.
Whether it’s a novel, a business report, an academic paper, or even a simple email, proofreading can significantly elevate the quality of your documents. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what proofreading is, why it’s important, and provide you with actionable tips and insights to perfect your proofreading skills.
So, let’s dive into the world where every comma counts and every word matters, beginning with an easy proofreading definition!
What is proofreading?
Proofreading is the final check of a text or content before it’s submitted. Proofreading is the process of reviewing the final draft of a text to ensure that all surface errors concerning grammar, punctuation, spelling, and formatting are corrected.
Think of proofreading as giving your writing a final shine to make sure it doesn’t have any mistakes. The key to understanding proofreading meaning is recognizing that it differs from editing, which involves more significant changes like restructuring and style adjustments.
Even though you’re document might have undergone copy editing or developmental editing, proofreading is your last chance to check for errors!
After understanding what is proofreading, we’ll move on to see why is proofreading important and whether is it really required.
Why is proofreading important?
Here are 5 reasons why proofreading is important and why you should do it:
1. Proofreading helps you catch mistakes like spelling errors or missing words so your writing is clear and easy to understand.
2. When you proofread your work, it shows that you take pride in what you’ve written and want to make sure it’s the best it can be.
3. Proofreading helps prevent silly mistakes that could make you look bad in front of others, like a teacher or a boss.
4. By fixing errors, proofreading ensures that your message is communicated accurately without any confusion.
5. With proofreading, you know your writing is error-free, and you feel more confident about sharing it with others, whether it’s for school, work, or fun.
Editing vs. proofreading: What’s the difference?
Editing involves making changes to enhance the content, including clarity, flow, structure, and style. It often requires rephrasing sentences, reorganizing paragraphs, and ensuring the content is coherent and engaging.
In contrast, proofreading focuses on correcting any remaining, surface-level errors in spelling, grammar, punctuation, and formatting. Unlike editing, it does not involve major content changes.
10 Proofreading tips for clear and error-free writing
Here are some practical tips to help you proofread more effectively:
1. Take a break before proofreading
After you finish writing, take a break. When you’ve been closely involved with a text, it’s easy to see what you intend to write rather than what you actually wrote. Stepping away from your work for a few hours, or even a day, helps you return with a fresh perspective.
2. Create a checklist
Develop a proofreading checklist of the most common errors you make. This may include items such as grammar, punctuation, spelling, formatting, and style. You can use Google Docs, MS Word, and Editpad to create such a checklist.
3. Read aloud
Reading your text aloud is remarkably effective. It forces you to slow down and lets you hear how your words sound together. You’ll catch not just typos and grammatical mistakes but also awkward phrasings and unclear sentences.
4. Print out your text and use a ruler or finger to guide your eyes
Print out your document, preferably in a larger font size and with double spacing, making it easier to mark corrections and make notes. Place a ruler under each line as you read, or use your finger to point at each word. This technique helps maintain your focus and reduces the chance of skipping over potential errors.
5. Check for one type of error at a time
If you try to identify every type of mistake in one go, you might miss more than you catch. Focus on one problem at a time—start with spelling, then check grammar, punctuation, and finally formatting. This segmented approach ensures thoroughness.
6. Watch out for homophones
Homophones are words that sound alike but have different meanings, such as “there,” “their,” and “they’re.” Spell check might not catch these, so pay extra attention to them.
7. Highlight errors
As you proofread, use colored pens, highlighters, or sticky notes to mark different types of errors or areas that need improvement. This visual system allows you to quickly identify patterns in your mistakes and prioritize your corrections. For example, you might use red for spelling errors, blue for grammar issues, and yellow for formatting inconsistencies. Punctuation errors can be subtle. Pay special attention to the use of commas, semicolons, colons, and apostrophes. Misplaced punctuation can change the meaning of a sentence dramatically.
8. Double-check names, numbers, and dates
Factual accuracy is crucial. Verify the spelling of names, the accuracy of numbers, and the correctness of dates. For professional documents, even a small mistake can create a bad impression.
9. Use proofreading tools wisely
Proofreading tools like Grammarly or Microsoft Word’s spell checker are helpful, but they’re not infallible. Use these tools to help identify obvious errors, but rely on your judgment for the final check. You can use grammar checkers, spell checkers, and punctuation checkers to proofread your document. Hemingway Editor, ProWritingAid, and QuillBot are some tools you can use.
10. Ask someone else to proofread
A fresh pair of eyes can catch errors you might have missed. If possible, have another person read your work. They might find mistakes you overlooked and can give you feedback on the clarity of your writing.
Proofreading examples
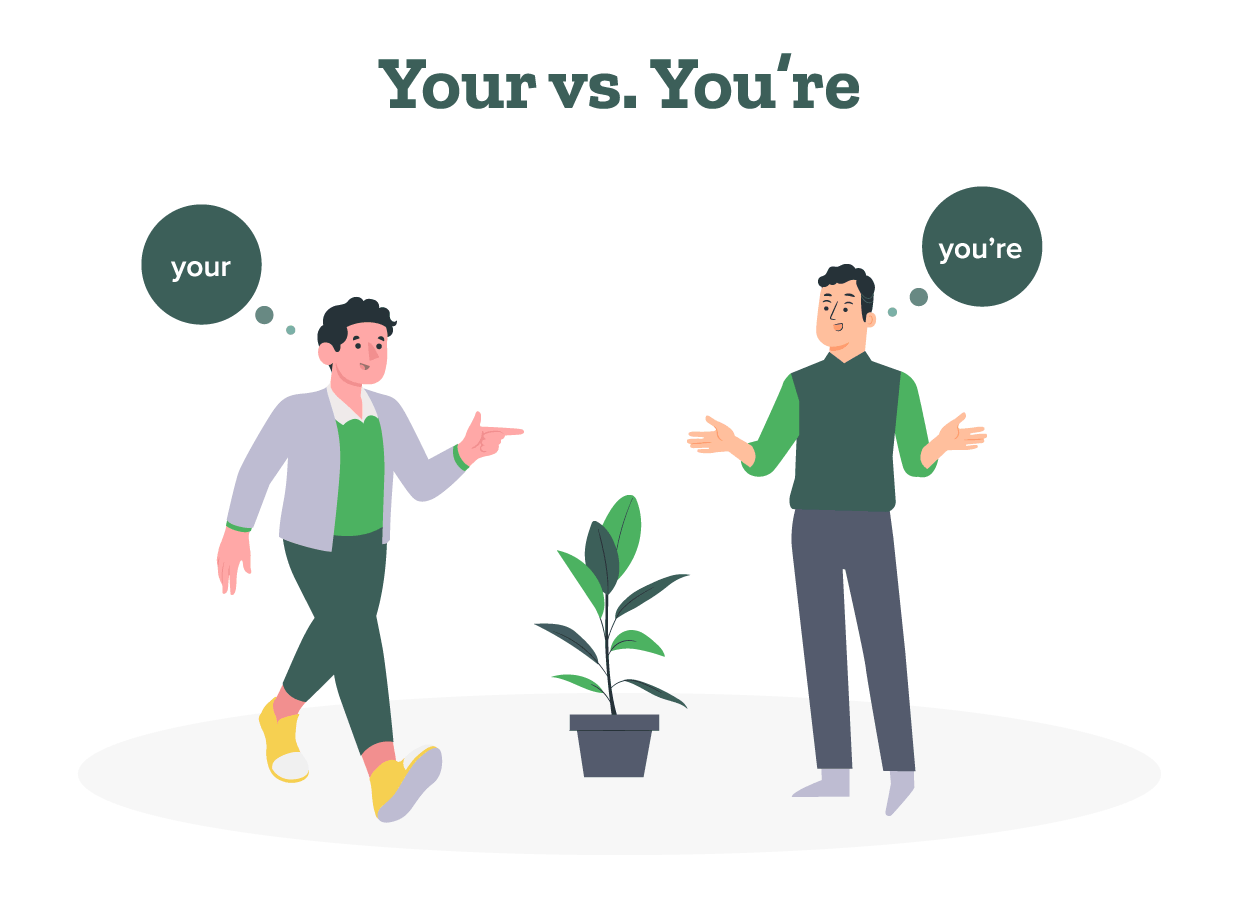
1. Your vs. you’re
Sentence: Your going to love the new updates.
Proofread and corrected: You’re going to love the new updates.
Explanation: “Your” is a possessive adjective, used to show ownership. “You’re” is a contraction for “you are.” This sentence requires “You’re” to convey the meaning “you are going to love,” indicating an action that is expected to happen.
2. Its vs. It’s
Sentence: Its important to check if it’s features work correctly.
Proofread and corrected: It’s important to check if its features work correctly.
Explanation: “It’s” is a contraction of “it is” or “it has”, and “its” is a possessive pronoun. In this sentence, “It’s” is needed as a contraction of “it is important,” and “its” is used to indicate possession of “features.”
3. Missing comma in a compound sentence
Sentence: I finished the report but he has not reviewed it yet.
Proofread and corrected: I finished the report, but he has not reviewed it yet.
Explanation: A comma is needed before “but” in a compound sentence. It separates two independent clauses, making the sentence easier to read and understand.
4. Incorrect punctuation with direct speech
Sentence: “How are you doing today” he asked.
Proofread and corrected: “How are you doing today?” he asked.
Explanation: The dialogue within the quotation marks is a question and should end with a question mark.
5. Misused apostrophe for plurals
Sentence: The company’s new policy’s affect all employee’s.
Proofread and corrected: The company’s new policies affect all employees.
Explanation: “Policies” is the plural form of “policy” and does not need an apostrophe. “Employees” is the plural of “employee” and also does not need an apostrophe. However, “company’s” correctly uses an apostrophe to show possession of the new policies.
How much does proofreading cost?
The cost to proofread ranges from $0.01 to $0.05 per word. Alternatively, some proofreaders charge by the hour, with rates generally ranging from $20 to $50 per hour. For larger projects, such as a book or thesis, proofreaders might offer a flat fee.
However, the cost can vary, depending on the document’s length, complexity, turnaround time, and the proofreader’s level of expertise. They also depend on the type of proofreading required, such as academic proofreading, translation proofreading, business proofreading, etc.
How long does proofreading take?
The time required for proofreading can depend on several factors, including the length of the document and the number of corrections needed. On average, a professional proofreader can proofread about 2000-3000 words per hour.
How to select the best proofreading service?
To select the best proofreading service, follow these brief steps:
1. Portfolio and experience
Select services specializing in your field, such as academic writing, business reports, or creative writing. Ask to see their previous work portfolio, request references from past clients, or look for previous work samples on their website.
2. Detailed pricing and invoicing
Compare pricing and choose a service that provides detailed pricing information, including per-word or per-page rates, minimum fees, formatting, and additional charges. Avoid services that have hidden fees or unclear pricing structures.
3. Turnaround time guarantees
Look for services that offer guaranteed turnaround times as per your deadline. Discuss your specific timeline requirements to ensure that they can accommodate your needs without rushing the proofreading process.
4. Sample edit and free trial
Request a sample edit or free trial from the service to assess the quality of their work firsthand. Provide a short excerpt from your document to proofread and evaluate the service’s credibility.
The following are the key attributes to look for in a skilled proofreader:
-
-
-
- Ability to spot even minor errors
- Grasp of grammar, syntax, and vocabulary
- Skill in meeting deadlines
- Familiarity with various word processing and editing software
- Understanding of cultural nuances and sensitivities in language
- Ability to explain changes and suggestions clearly and diplomatically
- Expertise in your specific field (e.g., medical, legal, technical)
5. Secure file handling and confidentiality
Look for services that use encrypted file transfers, secure storage systems, and confidentiality agreements to protect your intellectual property. If your text contains sensitive or confidential information, consider getting a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) signed.
6. Revision policy and customer support
Select a service that provides a clear revision policy and responsive customer support. Find out how many rounds of revisions are included and the procedure for requesting changes or clarifications. Test the service’s customer support by asking questions or submitting inquiries before placing an order. This will help you evaluate their responsiveness.
A company that has all these benefits and provides exceptional proofreading services is PaperTrue. We provide expert editing and proofreading services and our team of experienced proofreaders ensures perfection.
With our quick turnaround times, competitive pricing, and satisfaction guarantee, you can trust PaperTrue to elevate your writing!
Keep reading for more useful resources:
- Novel Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Manuscript Proofreading | Definition, Process & Standard Rates
- Screenplay Proofreading: Importance, Process, & Cost
- Script Proofreading: Rates, Process, & Proofreading Tips
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
-
-